Introduction
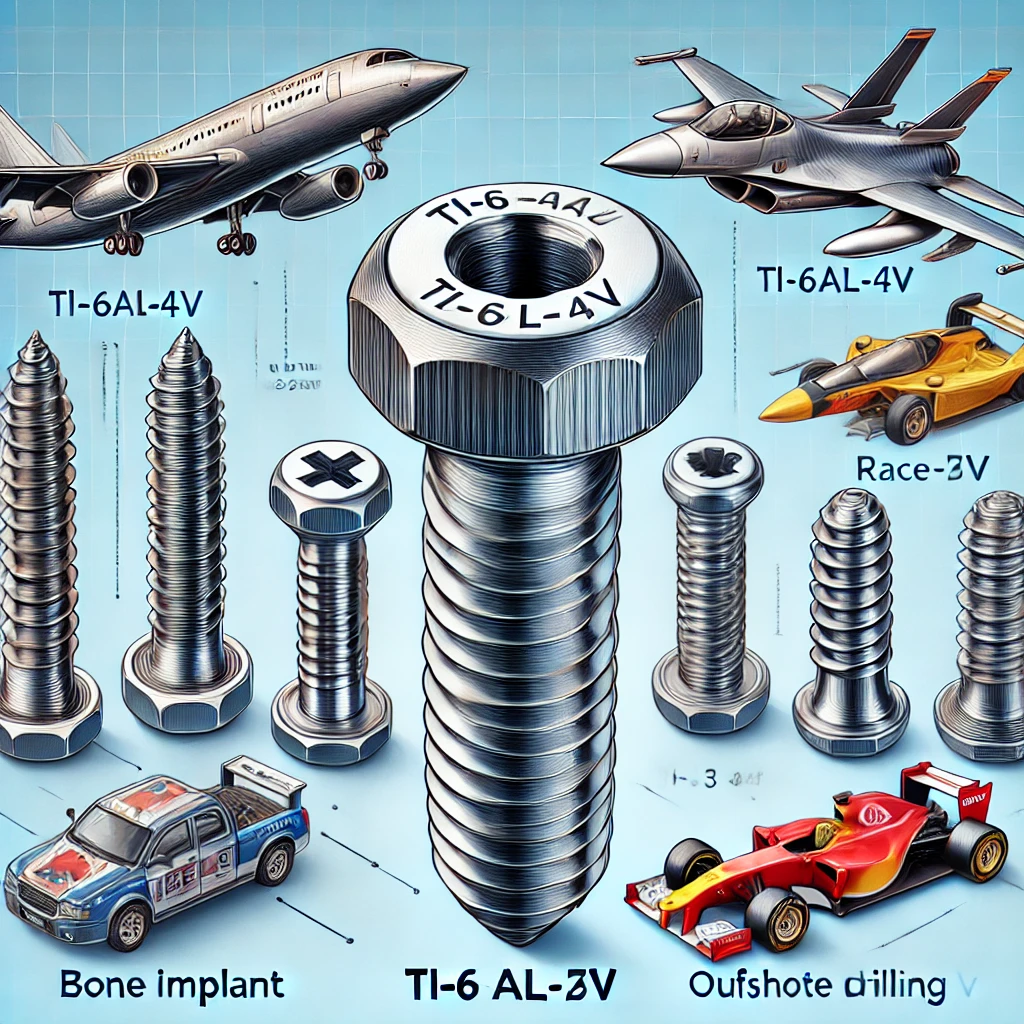
Titanium screws are widely used in industries that require high strength, corrosion resistance, and lightweight properties. Their superior mechanical and chemical characteristics make them indispensable in aerospace, medical, automotive, and marine applications. This article explores the titanium screw composition, manufacturing process, applications, and top global manufacturers.
Material Composition
Titanium screws are typically made from the following titanium alloys:
| Alloy | Composition | Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5) | 90% Ti, 6% Al, 4% V | High strength, corrosion resistance, lightweight |
| Ti-6Al-4V ELI (Grade 23) | 90% Ti, 6% Al, 4% V | Biocompatibility, high fracture toughness |
| Commercially Pure Titanium (Grades 1-4) | 99% Ti | Excellent corrosion resistance, moderate strength |
| Ti-3Al-2.5V (Grade 9) | 92% Ti, 3% Al, 2.5% V | Good weldability, high strength-to-weight ratio |
Titanium Screw Manufacturing Process
The production of titanium screws involves multiple stages to ensure precision and durability. The key steps include:
1. Material Selection and Preparation
Titanium billets or rods are selected based on the required alloy specifications. The raw material undergoes chemical and mechanical testing to ensure compliance with industry standards.
2. Forging and Forming
Titanium is forged into desired shapes using high-temperature forming techniques. Extrusion and rolling processes refine the metal’s grain structure for enhanced mechanical properties.
3. Machining and Threading
Screws are precision-machined using CNC (Computer Numerical Control) lathes and thread-rolling machines to ensure accurate dimensions and thread integrity.
4. Heat Treatment
Heat treatment improves mechanical strength and stress resistance. The process typically includes solution treatment and aging, particularly for high-strength alloys like Ti-6Al-4V.
5. Surface Treatment
To enhance performance, titanium screws undergo surface treatments such as anodization, passivation, or plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO). These treatments improve corrosion resistance and reduce friction.
6. Quality Control and Testing
Non-destructive testing (NDT) methods, including ultrasonic testing, X-ray inspection, and tensile testing, are performed to verify structural integrity and material properties.
Applications of Titanium Screws
Titanium screws are critical in various industries due to their exceptional strength, lightweight design, and corrosion resistance.
Aerospace
- Fastening structural components in aircraft and spacecraft
- High-temperature resistance in jet engines
- Weight reduction for fuel efficiency improvement
Medical
- Orthopedic implants (bone screws, dental implants)
- Biocompatibility ensures minimal rejection in the human body
- Spinal fixation systems and reconstructive surgeries
Automotive
- High-performance racing car components
- Weight reduction for improved fuel efficiency
- Heat resistance in high-performance engines
Marine
- Corrosion-resistant fasteners for offshore structures
- Submarine and naval vessel applications
- Ship propellers and engine components
Industrial & Chemical Processing
- Chemical plants exposed to aggressive environments
- Fasteners for heat exchangers and pressure vessels
- High-temperature resistance for industrial equipment
Top Titanium Screw Manufacturers Worldwide
Several key players dominate the titanium fastener market worldwide:
| Company | Country | Specialization |
| Precision Castparts Corp. | USA | Aerospace-grade titanium fasteners |
| Lisi Aerospace | France | High-performance aerospace and automotive fasteners |
| Böllhoff Group | Germany | Industrial and lightweight fastener solutions |
| TriMas Corporation | USA | Aerospace and automotive titanium fasteners |
| Shanghai Tianbao Fastener Manufacturing | China | Medical and industrial fasteners |
| Toray Industries | Japan | High-tech composite and titanium fasteners |
Case Studies: Real-World Applications of Titanium Screws
To further illustrate the importance of titanium screws, the following case studies highlight real-world applications:
Case Study 1: Titanium Screws in Aerospace – Boeing 787 Dreamliner
Boeing extensively utilizes titanium fasteners in the 787 Dreamliner to reduce weight and enhance fuel efficiency. Traditional steel fasteners were replaced with titanium screws, leading to weight reduction, improved corrosion resistance, and lower maintenance costs. This transition improved fuel efficiency by nearly 20% compared to previous models.
Case Study 2: Medical Industry – Titanium Screws in Orthopedic Surgery
A clinical study involving 500 patients with tibial fractures found that titanium screws provided superior biocompatibility, reducing post-surgical complications such as infections and allergic reactions. Compared to stainless steel alternatives, patients exhibited improved healing rates and long-term stability, with a 30% reduction in revision surgeries over five years.
Case Study 3: Automotive Industry – Formula 1 Applications
Formula 1 teams use titanium fasteners to improve vehicle performance. A case from Scuderia Ferrari revealed that replacing steel screws with titanium reduced the car’s weight by several kilograms, allowing for faster acceleration and better handling. Titanium’s exceptional heat resistance ensured the screws maintained integrity under extreme racing conditions.
Case Study 4: Marine Applications – Offshore Drilling Rigs
Titanium screws are used in offshore drilling rigs due to their exceptional corrosion resistance. A study on a North Sea oil platform showed that replacing conventional steel fasteners with titanium increased the lifespan of critical structures exposed to harsh marine environments. This transition resulted in a 40% reduction in maintenance costs and minimized operational downtimes.
Conclusion
Titanium screws offer an unparalleled combination of strength, corrosion resistance, and lightweight properties, making them essential in high-performance applications across multiple industries. As technology advances, innovations in material science and manufacturing will continue to enhance the efficiency and affordability of titanium fasteners, expanding their usage in emerging sectors.
The real-world case studies demonstrate how titanium screws improve efficiency, safety, and longevity in aerospace, medical, automotive, and marine industries. With increasing demand for lightweight and high-strength materials, titanium screws are expected to play a crucial role in the future of engineering and advanced manufacturing.




